What is WiFi? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding WiFi Technology
WiFi is an essential technology that enables wireless communication between devices, allowing them to connect to the internet or communicate with each other without physical cables. From smartphones and laptops to smart home gadgets like security cameras, WiFi plays a vital role in our daily digital interactions. In this article, we’ll explore what WiFi is, how it works, different types of WiFi, and how to set up and optimize your WiFi network for maximum performance.
1. What is WiFi?
WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) is a wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to transmit data over short distances. It allows devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets to connect to the internet and communicate with each other without needing a wired connection.
WiFi works using the IEEE 802.11 standards, a set of protocols defining how data is transmitted wirelessly. WiFi networks are common in homes, businesses, and public spaces, offering easy internet access without the need for cables.
2. How Does WiFi Work?
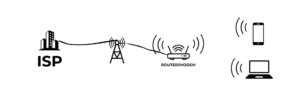
WiFi relies on a central hub—typically a wireless router—that transmits data using radio waves. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Internet Connection: The router connects to an Internet Service Provider (ISP) via a modem.
- Data Transmission: The router emits radio signals that allow nearby devices to connect to the internet.
- Device Connection: Devices equipped with WiFi (like laptops or smartphones) connect to the router by searching for its wireless signal and entering the appropriate password.
- Wireless Communication: The router facilitates the transmission of data between the connected devices and the internet, allowing users to browse websites, stream videos, and more.
WiFi signals can travel up to several hundred feet, but their strength can weaken due to obstacles like walls or interference from other devices.
3. WiFi Standards Explained
WiFi technology has evolved over the years, offering improvements in speed, range, and capacity. Below is a brief overview of key WiFi standards:
- 802.11b/g (WiFi 1-3): Early WiFi standards with relatively slow speeds (up to 54 Mbps) and limited range.
- 802.11n (WiFi 4): An improvement in speed (up to 600 Mbps) and coverage.
- 802.11ac (WiFi 5): A significant upgrade with speeds up to 1 Gbps and support for multiple devices.
- 802.11ax (WiFi 6): The latest standard offering enhanced speed, performance in crowded environments, and energy efficiency. It also reduces latency for a better overall experience.
- WiFi 6E: An extension of WiFi 6, which introduces a new 6 GHz band, allowing faster connections and reduced interference.
- WiFi 7: Offers even faster speeds, better support for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and ultra-low latency.
4. Frequency Bands: 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz vs. 6 GHz
WiFi operates on multiple frequency bands, each with unique characteristics:
- 2.4 GHz Band:
- Pros: Greater range, better at penetrating walls and obstacles.
- Cons: Slower speeds and more susceptible to interference from devices like microwaves and cordless phones.
- 5 GHz Band:
- Pros: Faster speeds, less interference.
- Cons: Shorter range and less effective at penetrating walls.
- 6 GHz Band: (Available with WiFi 6E)
- Pros: Extremely fast speeds and minimal interference.
- Cons: Shorter range and primarily for advanced devices.
5. Public vs. Private WiFi Networks
- Public WiFi: Found in places like cafes, airports, and libraries. While convenient, public networks often lack strong security measures. Always use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) when accessing sensitive information over public WiFi.
- Private WiFi: Typically found in homes and businesses, these networks are secured with encryption (WPA2/WPA3) and require a password. Private networks are safer for conducting secure transactions and sharing sensitive data.
6. Advantages and Disadvantages of WiFi
Advantages:
- Convenience: Access the internet wirelessly within the range of a WiFi network.
- Mobility: Freedom to move around while staying connected.
- Ease of Setup: Requires minimal hardware, making setup quick and hassle-free.
- Supports Multiple Devices: Can connect several devices simultaneously, from phones to smart home gadgets.
Disadvantages:
- Signal Interference: Electronic devices and physical barriers can weaken WiFi signals.
- Limited Range: WiFi signals weaken with distance, and may not cover large areas without additional equipment like extenders.
- Security Concerns: Without proper encryption, WiFi networks are vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized access.
- Variable Speeds: Performance may vary depending on signal strength, network congestion, and the number of connected devices.
7. Setting Up a WiFi Network: Step-by-Step Guide
- Connect the Router: Plug the router into the modem provided by your ISP.
- Access the Router Settings: Use a web browser to configure the network name (SSID) and set a strong password.
- Enable Encryption: Choose WPA3 or WPA2 encryption for maximum security.
- Place the Router Strategically: Put the router in a central location, away from walls and interference.
- Extend Coverage: If the signal is weak in some areas, use WiFi extenders or a mesh system.
8. Common WiFi Problems and Solutions
- Slow Speeds: Check for interference from other devices or switch to a less congested channel (5 GHz). Restarting the router or upgrading firmware often resolves speed issues.
- Dropped Connections: Reposition the router or check if firmware updates are available.
- Weak Signal: Use extenders or mesh networks to improve coverage.
9. The Future of WiFi
WiFi technology is continuously evolving. WiFi 6E is already here, introducing the 6 GHz band, which provides more bandwidth and faster speeds. WiFi 7, set to arrive soon, will further increase speeds, reduce latency, and support more IoT devices, making it ideal for smart homes and high-demand applications like gaming and 8K video streaming.
10. FAQs on WiFi Setup and Optimization
- Do I need to pay for WiFi? Yes, most ISPs charge a monthly fee for internet access. However, once you have a router and modem, WiFi access within your home or business is free.
- How can I improve my WiFi signal? Place your router in a central location, update the firmware, and use a WiFi extender or mesh network to extend coverage.
- How secure is WiFi? Private WiFi networks using WPA3 encryption are highly secure. Always use strong passwords and avoid using public WiFi for sensitive activities without a VPN.
6 Best WiFi Routers for Your Home or Business
Choosing the right WiFi router can significantly impact the speed, range, and stability of your wireless network. Here are some of the top routers for different needs, ranging from basic home use to more advanced enterprise setups.
1. TP-Link Archer AX73 (Best Overall)
- Key Features:
- Supports WiFi 6 (802.11ax)
- Speeds up to 5400 Mbps
- Dual-band (2.4 GHz + 5 GHz)
- 6 antennas for extended coverage
- MU-MIMO and OFDMA for efficient data transmission
- Why It’s Recommended: Ideal for homes with multiple devices, this router delivers fast speeds, excellent coverage, and stable connections even in crowded environments.
2. Netgear Nighthawk AX12 (Best for Streaming and Gaming)
- Key Features:
- WiFi 6 with speeds up to 6 Gbps
- Tri-band support (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 5 GHz)
- 8 high-performance antennas
- Built-in security (Netgear Armor)
- 12-streams for smooth 4K/8K streaming and gaming
- Why It’s Recommended: This is an excellent choice for gaming enthusiasts and heavy streamers. Its tri-band technology reduces network congestion, ensuring smooth, high-speed connections.
3. Google Nest WiFi (Best for Mesh Systems)
- Key Features:
- Dual-band WiFi with speeds up to 2200 Mbps
- Mesh system for large coverage areas (expandable with additional nodes)
- Built-in Google Assistant smart speaker in each node
- Automatic updates and network security
- Why It’s Recommended: Perfect for large homes or offices, the Google Nest WiFi system provides seamless coverage across multiple rooms or floors, eliminating dead spots with its mesh network.
4. Asus ROG Rapture GT-AX11000 (Best for Power Users)
- Key Features:
- WiFi 6 with speeds up to 11 Gbps
- Tri-band with Game Boost feature for prioritizing gaming traffic
- 8 antennas for maximum range and signal strength
- Advanced network security with AiProtection Pro
- Why It’s Recommended: This powerhouse router is designed for gamers and tech enthusiasts who need ultra-fast speeds and advanced features like traffic prioritization and comprehensive security.
5. TP-Link Deco X68 (Best Budget Mesh System)
- Key Features:
- WiFi 6 with speeds up to 3600 Mbps
- Dual-band mesh system for wide coverage
- Seamless roaming between nodes
- Easy setup with TP-Link app
- Why It’s Recommended: If you’re looking for a cost-effective solution to cover a large area, this mesh system offers good performance at an affordable price. It’s ideal for families or small offices.
6. Linksys Velop MX10 (Best for Large Homes)
- Key Features:
- Tri-band WiFi 6 with speeds up to 5.3 Gbps
- Covers up to 6,000 square feet (expandable with additional nodes)
- 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
- App-based setup and control
- Why It’s Recommended: With extensive coverage and great performance, the Linksys Velop is perfect for large homes or small businesses needing robust WiFi across multiple floors or rooms.
How to Choose the Right WiFi Router
When selecting a WiFi router, consider the following factors to find the best match for your needs:
- Speed: Look for routers that support at least WiFi 5 (802.11ac) or the newer WiFi 6 (802.11ax) standards for faster speeds and better performance with multiple devices.
- Coverage: Ensure the router’s coverage matches your space. Larger homes or offices may benefit from mesh systems like Google Nest WiFi or TP-Link Deco.
- Number of Devices: Choose a router that can handle the number of devices you plan to connect. WiFi 6 routers are better equipped for high-traffic environments.
- Features: Prioritize routers with advanced features like MU-MIMO, OFDMA, and beamforming for optimal data transmission and range.
- Security: Built-in security features, such as WPA3 encryption and parental controls, provide enhanced protection for your network.